Since its inception in 1988, Bluetooth has undergone several iterations, each introducing new features that enhance the performance of the wireless communication protocol to unlock new use cases and optimize the current ones.
Also read: Bluetooth version differences
For instance, version 5.1 enhanced location and tracking calculation using AoA and AoD, while 5.2 focused on low-energy audio streaming. Versions 5.3 and 5.4 primarily enhanced device networking with periodic advertising.
The latest iteration (Bluetooth version 6.0) was launched on 3rd September 2024, and it introduces 6 new features, of which one provides a significant advantage.

I’ll explain these features and show you why the channel-sounding aspect is particularly important for distance measurement accuracy and secure access. Let’s get started!
New Bluetooth 6.0 Features
Bluetooth Channel Sounding
This feature introduces true distance awareness by enabling two-way ranging between two BLE devices, making distance measurement accurate to within 10 cm. Channel sounding also brings onboard a robust security layer to ensure only authorized users can access secure areas (such as unlocking doors) when within range. More on this feature later.

Decision-Based Advertising Filtering
Decision-based advertising filtering is used when scanning. It allows the scanning device to use the content of a packet received on the primary advertising channel to determine if it is necessary to scan for related packets on secondary channels. This enhances scanning efficiency by reducing the time taken to check data packets on secondary channels that might not have the relevant PDUs to the running application.
Also read: how does BLE beacon works?
Monitoring Advertisers
Like decision-based advertising filtering, this feature improves the scanning efficiency of a Bluetooth device. But it uses the Host Controller Interface (HCI) to monitor and inform the host when devices of interest move in and out of range.
ISOAL Enhancement
Bluetooth 6.0 improves the Isochronous Adaptation Layer (ISOAL) by defining a new data framing model that reduces latency and gives better reliability if producing framed PDUs (Protocol Data Units).
LL Extended Feature Set
This feature allows devices to exchange their shared link-layer feature information that they both support.
Frame Space Update
Instead of using a defined constant value of 150 µs to separate the adjacent packet transmissions in connected events or CIS (Connected Isochronous Stream) subevents, this frame spacing update negotiates the timing separation to optimize throughput. It can now be longer or shorter.
Why Bluetooth Channel Sounding Is The Biggest 6.0 Bluetooth Upgrade?
Bluetooth channel sounding is the most significant upgrade in Bluetooth version 6.0 because it brings forth these 3 benefits to developers.
- Accuracy: Channel sounding utilizes multi-channel PBR (Phase-Based Ranging) to make the ranging capabilities between two connected devices as accurate as possible. So while AoA and AoD in the previous versions (from 5.1) had sub-meter level accuracy, channel sounding provides centimeter-level accuracy across considerable distances. This introduces true distance awareness, which is critical when developing tracking and monitoring solutions for assets and employees.
- Security: Security is paramount as the number of BLE-connected devices increases in networks. Channel sounding features robust, multilayer security in the form of secondary ranging RTT (Round-Trip Time) secure distance bounding. This additional protection layer helps to thwart sophisticated MITM (Man-In-The-Middle) relay attacks in deployed solutions.
- Ubiquity: Bluetooth is present in all major consumer devices, so this update can introduce true distance awareness without needing new radio technology designs, additional hardware components, or hardware space. Interoperability should only be enforced through a formal qualification program.
With these benefits, Bluetooth 6.0 channel sounding is handy in the following use cases.
“Find My” Solutions
Bluetooth tags introduced the find my item phenomenon but currently, several devices embed this capability. With 6.0 Bluetooth, all connected devices can potentially be tags or “find my” devices. Developers can now introduce true distance awareness to these devices to make it easy to locate lost items with centimeter-level precision.
Digital Keys
Bluetooth digital keys provide a more secure locking mechanism for car doors, safes, gates, building access, etc. Bluetooth 6.0 makes this digital access system more secure and enhances the user experience by ensuring the lock only opens when the authorized digital key is within range.
Controllers, Mice, Earphones, and Keyboards
These devices run on batteries and can drain quickly if operating in active mode throughout. With channel sounding, they can accurately switch between active and inactive modes based on their distance from the host device.
Bluetooth HMIs
Bluetooth HMIs can accurately enhance personnel safety by only allowing usage from a safe distance.

How Bluetooth Channel Sounding Works
Much has been said about channel sounding in version 6.0 Bluetooth, but how does it actually work to achieve its benefits? Well, it incorporates these two technologies to enable secure, fine ranging between the connected devices.
Phased-Based Ranging (PBR)
PBR is responsible for accurate distance measurement, and it involves communication using multiple frequencies. The initiator sends a signal to the reflector using a specific frequency, and the receiver or reflector sends it back at the same frequency it came in.
Once it arrives back, the initiator calculates the distance between itself and the reflector using the phase difference between the sent and received signal.
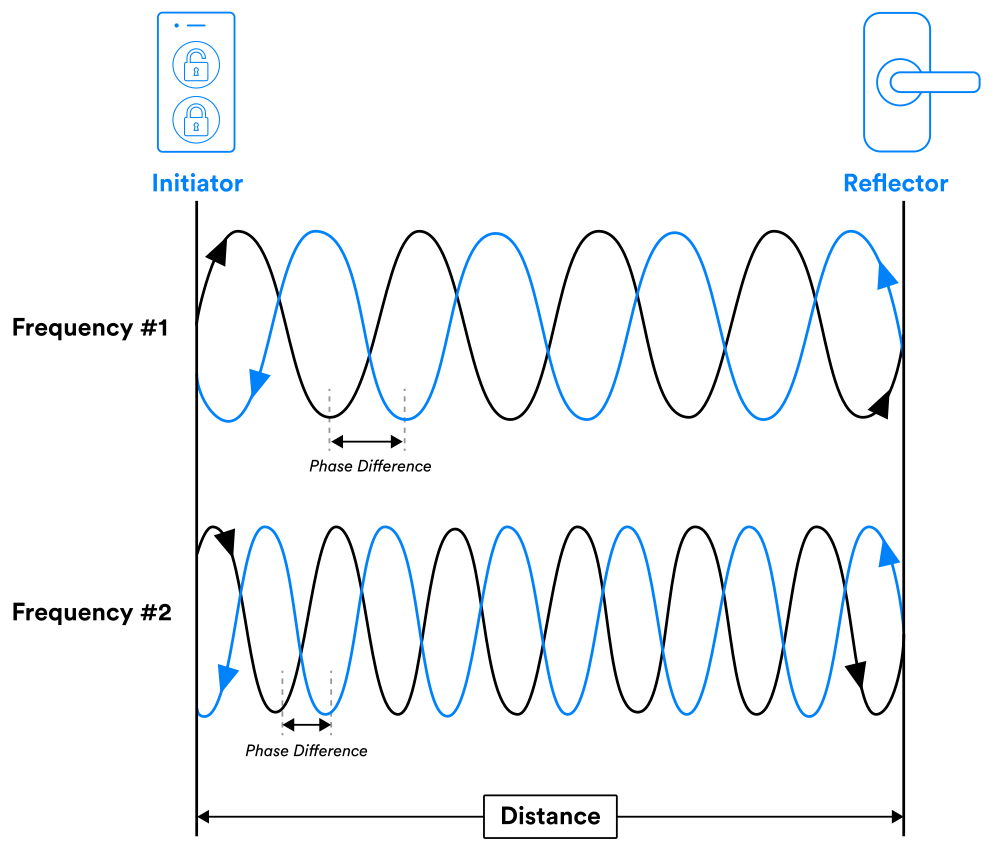
This transmission and reflection is repeated across different frequencies to give more accurate data about the distance between the two devices (especially where there are reflections) using the phase differences of each signal.
PBR can coordinate up to 72 channels (frequencies) in the 2.4GHz spectrum using 1–4 antenna paths between the connected devices. Even though one is enough, these extra antenna signal paths allow signals to pass through alternative routes if there’s interference.
Round-Trip-Time (RTT)
RTT is a secondary ranging method that is used for secure distance bounding to countermeasure sophisticated MITM relay attacks. With this technology, the initiator sends cryptographically scrambled data packets to the reflector, which then sends them back.
The initiator uses the ToF (Time of Flight) to calculate the distance between the two, which requires the ToA (Time of Arrival) and ToD (Time of Departure) to be recorded in both to get the difference for distance calculation.
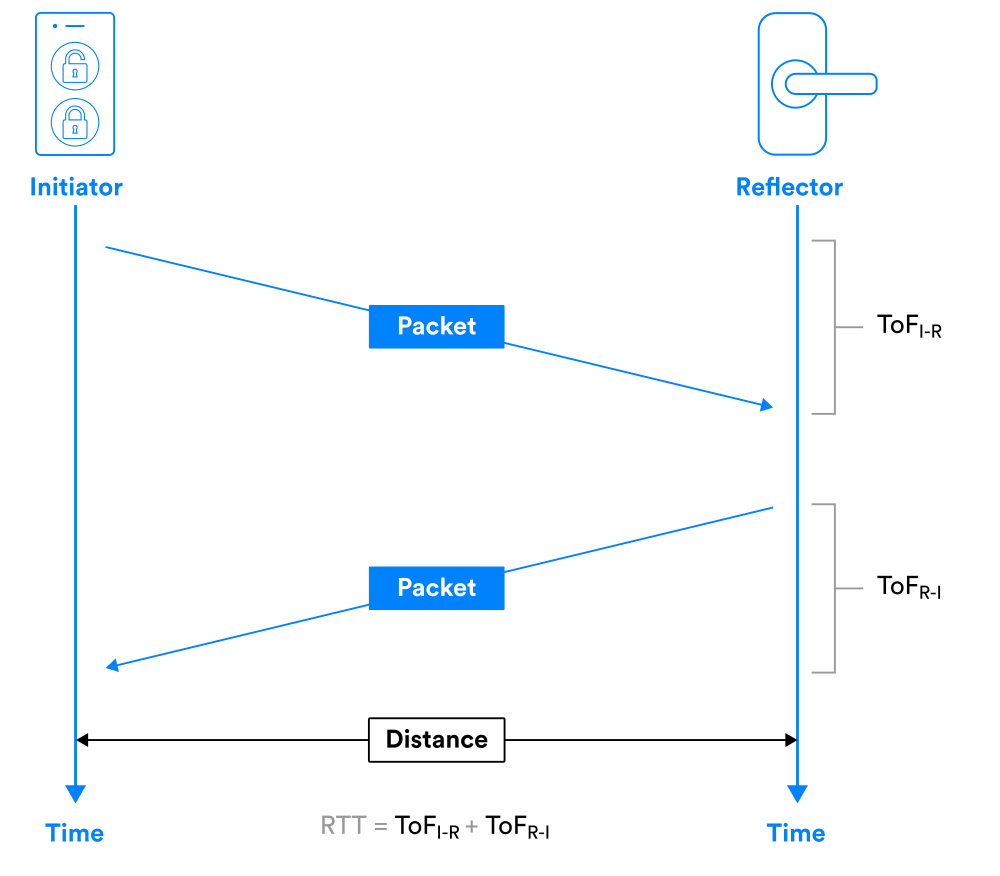
This secure distance bounding technique provides an independent avenue for cross-checking PBR. It can also provide setup and calibration processes to compensate for the clocking differences between the devices.
Bluetooth 6.0 combines these two in the channel sounding feature to make distance measurement accurate and precise.
Will Bluetooth Channel Sounding Make RSSI and Direction Finding Obsolete?
The answer is yes and no. Let me first explain what RSSI and direction-finding are to justify my answer.
RSSI
Introduced in version 1.1, Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) is the oldest Bluetooth-ranging technology. It calculates the distance between two connected devices using the measured signal strength between the two (amplitude). The more the amplitude decays, the further the distance between them.
This technology is well established in all smartphones but has a low accuracy of about 3–5 meters, which is due to interference from external factors that absorb and diffract the signal.
But RSSI’s accuracy can be improved by characterizing the RF environment and using multiple beacons, although not to the centimeter level.

Direction Finding (AoA and AoD)
Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD) significantly improved Bluetooth’s ranging accuracy by measuring or estimating the angle of the incoming and outgoing radio signals, then using trigonometry to calculate the distance.
AoA relies on the receiver’s antenna array to get the phase shift of the received signal to calculate its angle. On the other hand, AoD attributes measurements from the antenna’s receiver to specific antennas in the transmitter to calculate the outgoing signal angle. Therefore, for AoD to work, the receiver must know the transmitter’s antenna array design, making it more sophisticated than AoA.
But in both cases, you’ll need multiple antennas, and the two can only achieve sub-meter accuracy, which can be worsened by reflections and obstacles.

Bluetooth Channel Sounding
As explained earlier, channel sounding uses the multichannel PBR phase difference calculation as the primary ranging method and RTT ToF as a secondary ranging method to cross-check PBR. So it is more precise and capable of centimeter-level precision.
And The Key Question: Will RSSI and Direction Finding Obsolete?
My answer was yes and no. Channel sounding in version 6.0 Bluetooth can make RSSI and direction finding obsolete due to its security and unprecedented centimeter-level accuracy.
But you might get better results using a hybrid setup that blends channel sounding with direction finding, RSSI, or all two.
These technologies can be implemented in a single chip and optimized to activate for the right tasks. RSSI, for instance, can begin to get a rough distance estimate, detect device presence, or determine proximity, followed by channel sounding for accurate distance calculation as the devices get close to each other.
Combining direction finding and channel sounding is also feasible because it provides both angle and ranging information.
So channel sounding might not make RSSI and direction finding obsolete.

Overview of Dusun IoT’s Bluetooth 6.0 Products
Dusun IoT has been a pioneer manufacturer of Bluetooth products since its inception in 2005. So with the release of Bluetooth 6.0, you can expect our hardware to integrate this updated wireless protocol to enhance performance in:
- Asset/personnel tracking and positioning
- BLE Gateway scanning to find BLE tags and beacons
- Creating secure geofences, smart locks, and keyless vehicle entry (V2D)
You can expect the initial enabling products for Bluetooth 6.0 like chips, stacks, and modules this year, and then the final consumer products like key fobs and tags (asset trackers) by early 2025.
These devices will be in two configurations:
- A single antenna board to run low-power applications like asset tracking
- A dual antenna board for size-constrained end devices, such as key fobs, for personnel tracking



















