IoT gateways are key elements of bringing legacy and next-gen devices to the Internet of Things (IoT). Gateways integrate many protocols for networking, help manage storage and edge analytics on the data, and facilitate data flow securely between edge devices and the cloud.
Edge computing is a way to streamline the flow of traffic from IoT devices and provide real-time local data analysis. This article will discuss what edge computing and IoT gateways integrated with edge computing capability.
What are IoT edge and edge computing?
The edge of the IoT is where the action is. Figure 1 shows a simple IoT system. As can be seen from the figure, the edge includes a wide array of sensors, actuators, devices, and gateways. The sensors/actuators/devices are often called edge devices.
An edge device is any piece of hardware that controls data flow at the boundary between two networks. Edge devices fulfill a variety of roles, depending on what type of device they are, but they essentially serve as network entry (or exit) points.
Some common functions of edge devices are the transmission, routing, processing, monitoring, filtering, translation, and storage of data passing between networks.
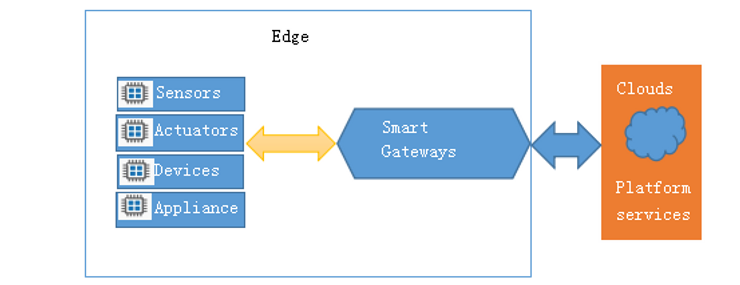
Figure 1 A simple IoT system
Unlike cloud computing, edge computing for the Internet of Things (IoT) allows IoT deployments to be enhanced through data processing closer to the end device.
Cloud computing is typically referred to in IoT use cases, where edge devices would collect data – sometimes massive amounts of it – and send it all to a data center or cloud for processing.
Edge computing triages the data locally so some of it is processed locally, reducing the backhaul traffic to the central repository.
Why IoT needs edge computing?
In Internet-of-Things we usually need to process a large amount of data coming from various sensors and devices. Previously, we send all data directly to the cloud and processed it there. But, this way may not be cost-efficient which means high latency, exposing privacy, and not being robust to connectivity issues.
As the IoT expands and there is a lot of data that need to be processed, it will take some time for the data to travel back and forth between the device and the data center if we use cloud computing. In some time-critical applications, cloud processing is unrealistic.
By storing and processing the data close to its source, we reduce the lag time and improve the overall app performance. As a result, we can analyze the data in real-time, without delays.
Edge computing not only reduces latency but potentially ensures that applications are not disrupted in case of limited or intermittent network connectivity. This can be very useful when applications are deployed in remote locations where network coverage is poor or even to reduce costs coming from expensive connectivity technologies like cellular technologies.
Data captured through edge devices may contain sensitive or private information. Running complex analytics in the cloud may expose privacy. With edge computing, an application can make sure that sensitive data is pre-processed on-site, and only data that is privacy compliant is sent to the cloud for further analysis, after having passed through the first layer of anonymizing aggregation.
Dusun’s Edge Computing Solution
Connections and management of many sensors/terminals and real-time analysis and processing of a large amount of data are challenges now. There may be different computing architectures according to different applications.
Considering many IoT edge devices have the weak computing power and need energy-saving, Dusun puts more emphasis on improving the computing power of the IoT gateways.
By designing and utilizing edge computing gateways, Dusun provides a common-sense edge computing gateway architecture as illustrated in figure 2.
The edge computing gateways gather IoT data from various sensors and devices, then run the user-defined applications to process the data. The processed data is then pushed to the cloud for further processing and finally used by various applications.
The edge computing gateway with edge computing can be flexibly equipped with apps to execute local policy and respond within milliseconds. This can be useful for many applications.
For example, running machine learning models directly on IoT edge gateway enables AI capabilities to be handled locally. Dusun’s smart edge computing gateways are programmable and support extended or secondary development.
Dusun provides SDKs and APIs which can be used to let customers make their programs to control the data processing and transfer procedure.

Figure 2 Dusun’s Edge Computing architecture
Summary
IoT edge devices control data flow at the boundary between two networks. As the IoT grows ever larger, data analysis and decision-making will have to localize—shifting from the cloud to the edge.
Edge computing brings computer data storage closer to the location where it is needed and allows IoT deployments to be enhanced through data processing closer to the end device. This results in lower latency and improved efficiencies in data transport. Sometimes, data privacy is also ensured through edge computing.
The Dusun edge computing solution focuses on the computing power of the IoT gateways which are often powered by an AC electric supply.
The edge computing gateways play a key role in the Dusun edge computing solution. The gateways collect data from various sensors/terminals and do data processing immediately.
They provide full-process industry/business services and support for innovative operations. The programmable ability makes the gateways suitable for many edge computing applications. If you are interested in edge computing gateways, more information can be found here.



















